Gluten-free diets have surged in popularity and necessity, driving a booming market for certified gluten-free foods all over the world. For food manufacturers, whether large, medium, or small the benefits of gluten-free certification are numerous.
In numbers
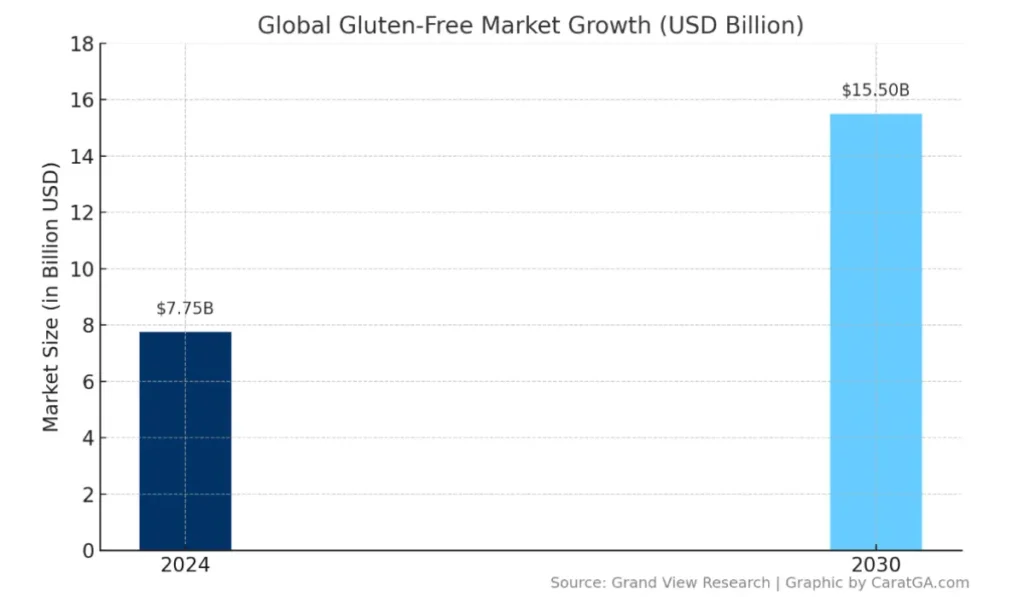
According to Grand View Research, in 2024, the global gluten-free products market was valued at roughly $7.75 billion, and this is projected to nearly double by 2030.
This CGA Insight explores the benefits of gluten-free certification for food companies, diving into:
- Benefits of gluten-free certification
- Major gluten‑free certification programs
- How important is the gluten-free logo
- How to apply for for gluten-free certification
Gluten‑Free Certification 101
Gluten-free certification is a process where food products are evaluated/tested to ensure they are gluten-free, according to the standards outlined by Codex Alimentarius in the U.S, Canada, and EU. In short, any product bearing a “Certified Gluten-Free” seal has undergone rigorous review of ingredients, production processes, and final gluten testing by a recognized certifying body.
Similar to many other identity preservation certification standards, the gluten-free standards are also based on the HACCP and ISO quality system guidelines to systematically prevent gluten contamination.
Benefits of Gluten-Free Certification
The primary benefits of gluten-free certification for food companies include:
1. It Increases Market Access
One of the most immediate benefits of gluten-free certification is expanded market access.
Certified gluten-free products appeal not only to the 1-2% of the population with celiac disease, but also to a wider audience who choose gluten-free for health or lifestyle reasons. Retail buyers and distributors often favor products with recognized gluten-free seals, as it simplifies their vetting process and reduces liability.
Furthermore, certified products are often listed in the certifier’s directories or mobile apps, essentially giving your product additional visibility to conscientious consumers who rely on these resources to find safe foodsaoecs.org.
2. It Builds Valuable Consumer Trust & Brand Loyalty
For millions of consumers, a gluten-free label on a food product is more than a marketing claim, it’s a matter of health and safety. Consumer trust is therefore paramount, and this is where certification delivers in spades. Displaying an official gluten-free certification logo on your packaging immediately signals to shoppers that an impartial authority has verified your product’s safety.
This assurance is invaluable to those with celiac disease or severe gluten sensitivity, who often stick to brands they trust. Earning a respected gluten-free seal can thus translate into increased customer loyalty and repeat sales.
3. It Ensures Regulatory Compliance
While gluten-free certification itself is voluntary from a legal standpoint, it serves as an added insurance policy for compliance. By following an accredited certification scheme, manufacturers greatly reduce the risk of inadvertently mislabeling a product or facing a recall due to hidden gluten. Many certified companies report improved overall food safety practices, which not only help with gluten but with other hazards too.
Major Gluten‑Free Certification Programs (and Their Standards)
Several certification programs are available globally, each with its own standards and recognition. Table 1 summarizes key gluten-free certification bodies, their administering organizations, core requirements, and geographic relevance:
| Administered By | Key Standard / Requirements | Primary Geographic Relevance |
| Celiac Canada (Canadian Celiac Association), in partnership with BRCGS | ISO 17021-1 management system certification; HACCP-based controls; <20 ppm gluten in finished product; annual independent audits. | North America (Canada, USA); expanding globally via the BRCGS network. |
| Gluten Intolerance Group (GIG) – USA | ISO 17065 certification scheme; requires <10 ppm gluten (stricter than 20 ppm); batch testing and plant inspections by accredited auditors. | North America (USA, Canada) and widely recognized internationally by manufacturers and consumers. |
| AOECS (Association of European Coeliac Societies) via national celiac societies (e.g. Coeliac UK) | Must meet EU Regulation 828/2014 definition of gluten-free (<20 ppm). | Europe (EU countries, UK, etc.) – accepted across AOECS member countries; recognized by gluten-free consumers worldwide. |
Table 1: Major gluten-free certification programs, their administering organizations, key requirements, and regional relevance for food manufacturers.
How Important Is the Gluten-Free Logo
A distinct gluten-free seal on the package makes a product stand out 90% of gluten-free consumers, all of whom are actively looking for a certification mark when shopping. In summary, this makes gluten-free certification a savvy business move to access high-growth markets and new revenue streams.
How to Apply for Gluten-Free Certification
Companies can apply for the CGA Gluten-Free Certification using the following steps:
| Step | Action | What You’ll Need |
| 1. Application Submission | Complete the CGA certification form and provide supporting documents. | Ingredient list, process flowcharts, allergen control plan, previous audits (if any). |
| 2. Document Review | Technical experts will assess your Gluten-Free Management System. | CGA aligns your program with ISO and Codex standards. |
| 3. Audit | A CGA auditor will conduct an in-depth facility inspection and sample testing. | Cross-contamination controls, sanitation SOPs, packaging review. |
| 4. Certification Decision | If compliant, CGA issues your certificate and authorizes use of the CGA Gluten-Free seal. | Certificate is valid for 1 to 3 years, with annual surveillance audits. |
Bundle Your Gluten-Free Audit
CGA has uniquely obtained the capability to provide integrated audits across multiple certification scopes. If you’re also pursuing Halal, Vegan, Non-GMO, or GFSI-level food safety standards (e.g., SQF), CGA can combine them into a single audit schedule.
To learn more, get in touch with a gluten-free certification specialist via +1 (331) 253-9610 or admin@caratga.com.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
No, gluten-free certification is not legally required. However, it serves as a powerful tool for building consumer trust and ensuring regulatory compliance. Certification significantly reduces the risk of mislabeling, cross-contamination, or recalls.
A certified gluten-free product has been verified by an independent third party through audits, lab testing, and documentation reviews to meet strict gluten-free standards (typically <20 ppm). In contrast, a self-declared gluten-free label does not require verification and may lack the same level of consumer confidence and retailer acceptance.
The certification process with Carat Global Assurance (CGA) typically takes 4–8 weeks, depending on the readiness of your documentation and facility. CGA’s streamlined process includes application submission, document review, a facility audit, and a certification decision.
Yes. CGA specializes in bundled audits, allowing you to combine gluten-free certification with Halal, Vegan, Non-GMO, GMP or GFSI-level audits (like SQF). This saves time, reduces costs, and minimizes audit fatigue for your team—especially valuable for manufacturers aiming to meet multiple compliance standards.
Gluten-free certification is available for a wide range of products, including packaged foods, beverages, ingredients, supplements, and even pet food. As long as your product contains less than 20 ppm gluten (or <10 ppm for stricter programs) and has proper allergen controls in place, it may qualify for certification through CGA.
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
Sources
Supporting information and quotations were drawn from:
- Regulatory guidelines
- Industry reports
- Celiac organisations (Celiac Disease Foundation on U.S labeling laws), Association of European Coeliac Societies on EU standards Official statements from gluten-free certification bodies such as Carat Global Assurance




